Limits of functions are essential to calculus and mathematical analysis, and are used to define continuity, derivatives, and integrals. We did not find results for Limit, restrict, circumscribe, confine mean to set bounds for
§1.5 | The Limit of a Function
Limit implies setting a point or line (as in time, space, speed, or degree) beyond which something cannot or is not permitted to go.
We want to give the answer 2 but can't, so instead mathematicians say exactly what is going on by using the special word limit
The limit of (x 2 −1) (x−1) as x approaches 1 is 2 Limits help us acknowledge the value of a function, not particularly at a specific input number, but at what approaches the number It is a powerful and evidently great tool to calculate the value of a function where direct substitution is not possible like dividing any number by zero. A limit indicates the value a function is approaching, not what it actually is
A limit can be determined by either substitution, function simplification, graphing, or through a calculator. Limit, mathematical concept based on the idea of closeness, used primarily to assign values to certain functions at points where no values are defined, in such a way as to be consistent with nearby values. In this chapter we introduce the concept of limits We may use limits to describe infinite behavior of a function at a point
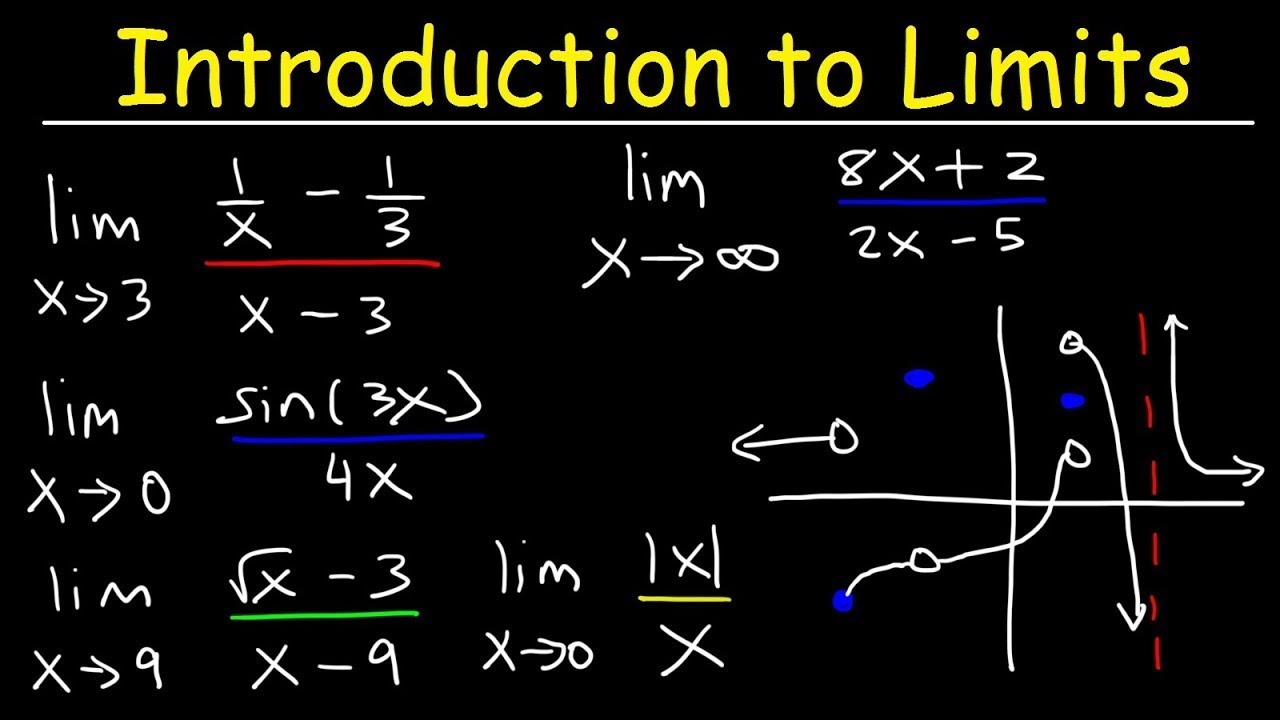
In this section, we establish laws for calculating limits and learn how to apply these laws.
Remember both parts of calculus are based on limits The limit of a function is the value that $$f (x)$$ gets closer to as $$x$$ approaches some number

